In order to determine the equation of a sinusoidal function, you need to find:
a - amplitude
b - affects the period
Period -
2π
/b/
c - horizontal shift
d - vertical shift
f(
x)=
asin
b(
x-c) +
d OR
f(
x)=
acos
b(
x+c) +
d
The equation could either be for a sine or cosine function
Example
State a sine equation for the function graphed below.
Steps
- First, we need to identify the Middle Axis. This determines if there is any up or down shifting - the d value.
Middle Axis =
Maximum + Minimum
2
Middle Axis = 3
+ (-1) = 1
2
Middle Axis is at y = 1
We can see that there is a vertical translation 1 unit up therefore, d = 1
2. Next, find the amplitude or the
a value. The amplitude is the distance between the middle axis and the maximum value. In this graph, the amplitude is 2.
3. Next find
b. But in order to find
b, we must determine the period of the function. To find the period, measure the distance along the x-axis between two maximum points or two minimum points.
Once you got the period, you can calculate for
b.
period = 2
π b =
2π b =
2π b = 1
period 2
π
4. Lastly, let's find the phase shift (horizontal shift) or
c. This is the trickiest value to find since there are many choices possible for c. But the question is asking for a sine equation. so we know that at
x = 0, the y-intercept is on the middle axis.
Let's recap the information we've determined:
a = 2
b = 1
c =
π/2
d = 1
Since the question is asking for an equation for a sine function, we will use the form
f(
x)=
asin
b(
x-c) +
d
Just plug the
a,
b,
c and
d values into the equation.
The final answer will be
f(x) = 2sin(x-π/2) + 1
Thank you for reading my post. I hope this helped you a bit and I wish you all the best in our final exam. Good luck and have a nice day!
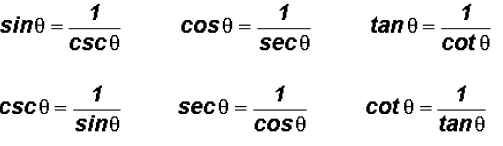
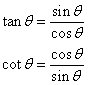



.jpeg)



